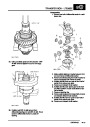
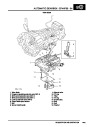
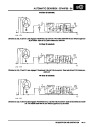
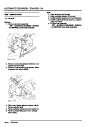
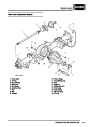
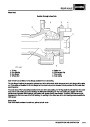
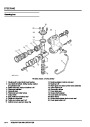
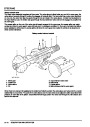
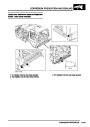
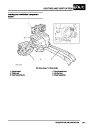
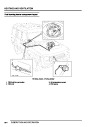
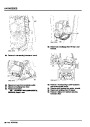
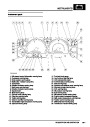
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
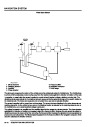
Operation - engine management
Fuel quantity
The ECM controls engine fuel quantity by providing sequential injection to the cylinders. Sequential injection allows
each injector to deliver fuel to the cylinders in the required firing order.
To achieve optimum fuel quantity under all driving conditions, the ECM provides an adaptive fuel strategy.
Conditions
Adaptive fuel strategy must be maintained under all throttle positions except:
l
l
l
l
Cold starting.
Hot starting.
Wide open throttle.
Acceleration.
All of the throttle positions mentioned above are deemed to be 'open loop'. Open loop fuelling does not rely on
information from the HO2 sensors, but the air/ fuel ratio is set directly by the ECM. During cold start conditions the
ECM uses ECT information to allow more fuel to be injected into the cylinders to facilitate cold starting. This strategy
is maintained until the HO2 sensors are at working temperature and can pass exhaust gas information to the ECM.
Because of the specific nature of the other functions e.g. hot starting, idle, wide open throttle, and acceleration they
also require an 'open loop' strategy. For NAS vehicles with secondary air injection for cold start conditions, refer to
the Emissions section.
+
EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary Air Injection System.
Adaptive fuel strategy also allows for wear in the engine and components, as well as slight differences in component
signals, as no two components will give exactly the same readings.
Function
To be able to calculate the amount of fuel to be injected into each cylinder, the ECM needs to determine the amount
of air mass drawn into each cylinder. To perform this calculation, the ECM processes information from the following
sensors:
l
l
l
l
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Crank speed and position (CKP) sensor.
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
During one engine revolution, 4 of the 8 cylinders draw in air. The ECM uses CKP sensor information to determine
that one engine revolution has taken place, and the MAF sensor information to determine how much air has been
drawn into engine. The amount of air drawn into each cylinder is therefore 1/4 of the total amount measured by the
ECM via the MAF sensor.
The ECM refers the measured air mass against a fuel quantity map in its memory and then supplies an earth path to
the relevant fuel injector for a period corresponding to the exact amount of fuel to be injected into the lower inlet
manifold. This fuel quantity is in direct relation to the air mass drawn into each cylinder to provide the optimum ratio.
During adaptive fuelling conditions, information from the heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) is used by the ECM to correct
the fuel quantity to keep the air/ fuel ratio as close to the stoichiometric ideal as possible.
Closed loop fuelling
The ECM uses a closed loop fuelling system as part of its fuelling strategy. The operation of the three-way catalytic
converter relies on the ECM being able to optimise the air/ fuel mixture, switching between rich and lean either side
of lambda one. Closed loop fuelling is not standard for all markets, vehicles that are not fitted with HO2S do not have
closed loop fuelling.
The ideal stoichiometric ratio is represented by λ =1. The ratio can be explained as 14.7 parts of air to every 1 part of
fuel.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-49
Product Specification
| Categories | Land Rover Defender, Land Rover Discovery II, Range Rover |
|---|---|
| Tags | Land Rover |
| Model Year | 1999 |
| Download File |
|
| Document Type | Workshop Manual |
| Language | English |
| Product Name | Discovery Series II |
| Product Brand | Land Rover |
| Document File Type | |
| Publisher | landrover.com |
| Wikipedia's Page | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Land_Rover |
| Copyright | Attribution Non-commercial |